
Basic Normal histology of fallopian tube YouTube
Last updated: May 12, 2019 Revisions: 21 format_list_bulleted Contents add The uterine tubes (or fallopian tubes, oviducts, salpinx) are muscular 'J-shaped' tubes, found in the female reproductive tract. They lie in the upper border of the broad ligament, extending laterally from the uterus, opening into the abdominal cavity, near the ovaries.
+histology+slide.jpg)
Histology Slides Database Fallopian Tube histology Slides
Fallopian Tube Chapter Outline Introduction 459 Anatomy, Histology, and Function of the Fallopian Tube 459 Anatomy 459 Histology 460 Mucosal Epithelial Alterations 461 Function 462 Approach to Examining Tubal Specimens 462 Bilateral Tubal Ligation for Sterilization 462 Salpingectomy for Tubal Ectopic Gestation 463

Fallopian Tube Histology Diagram Quizlet
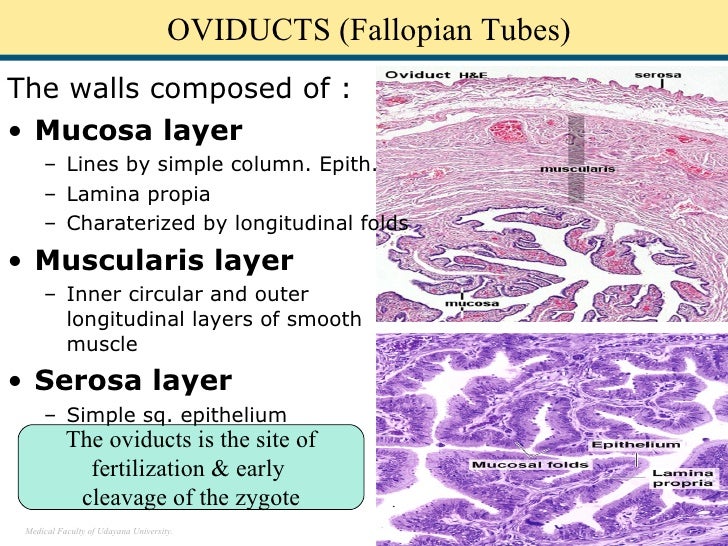
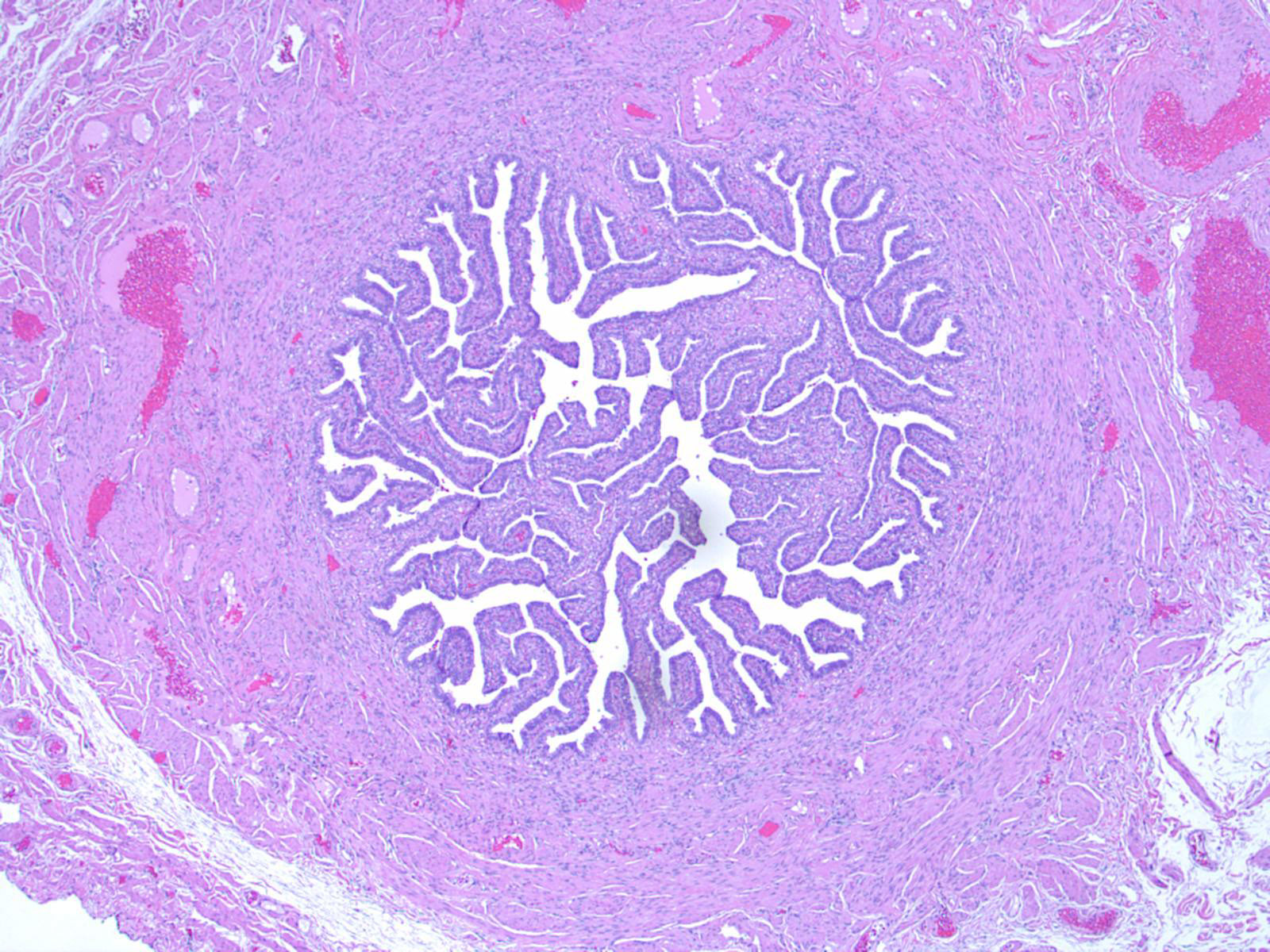
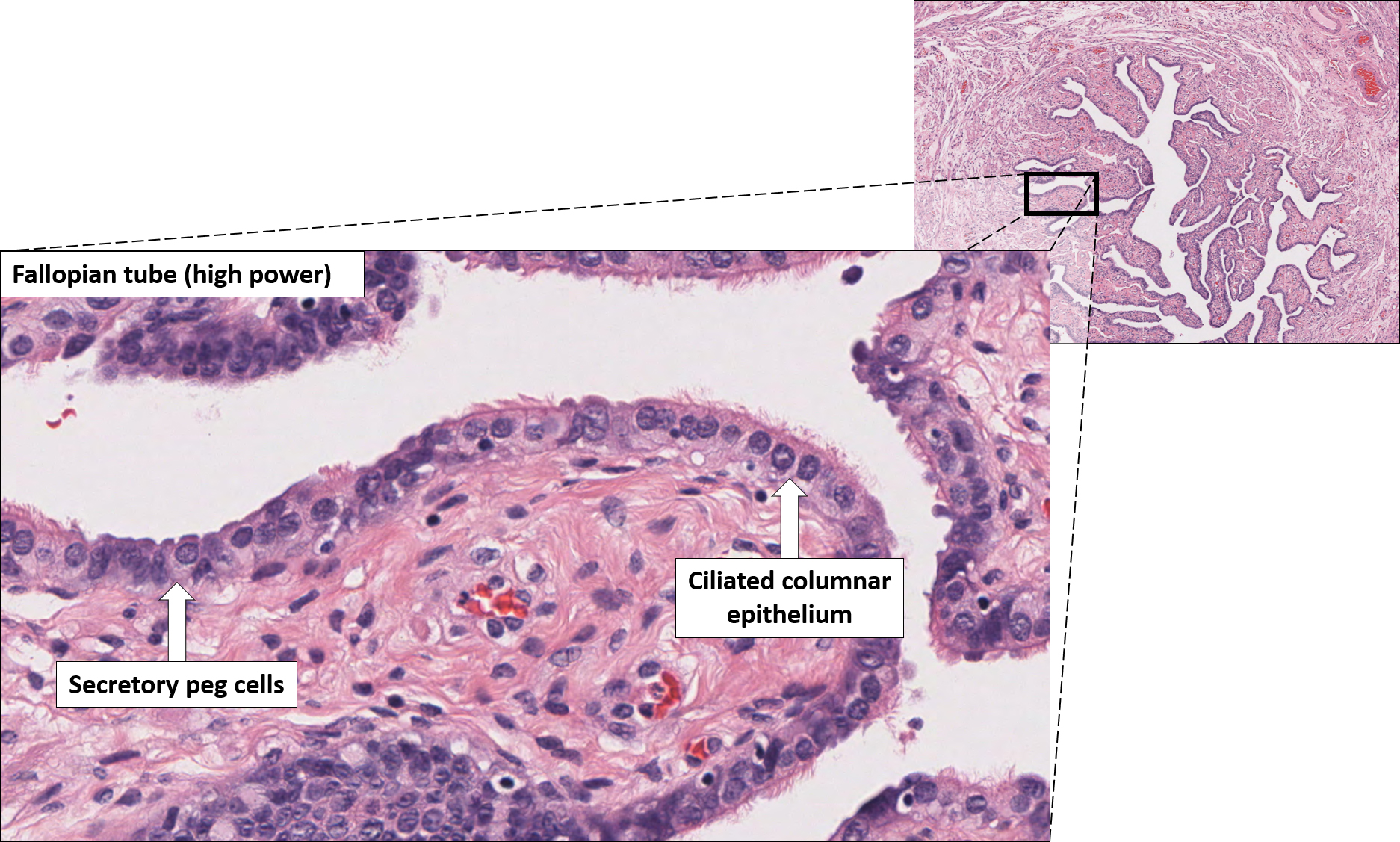
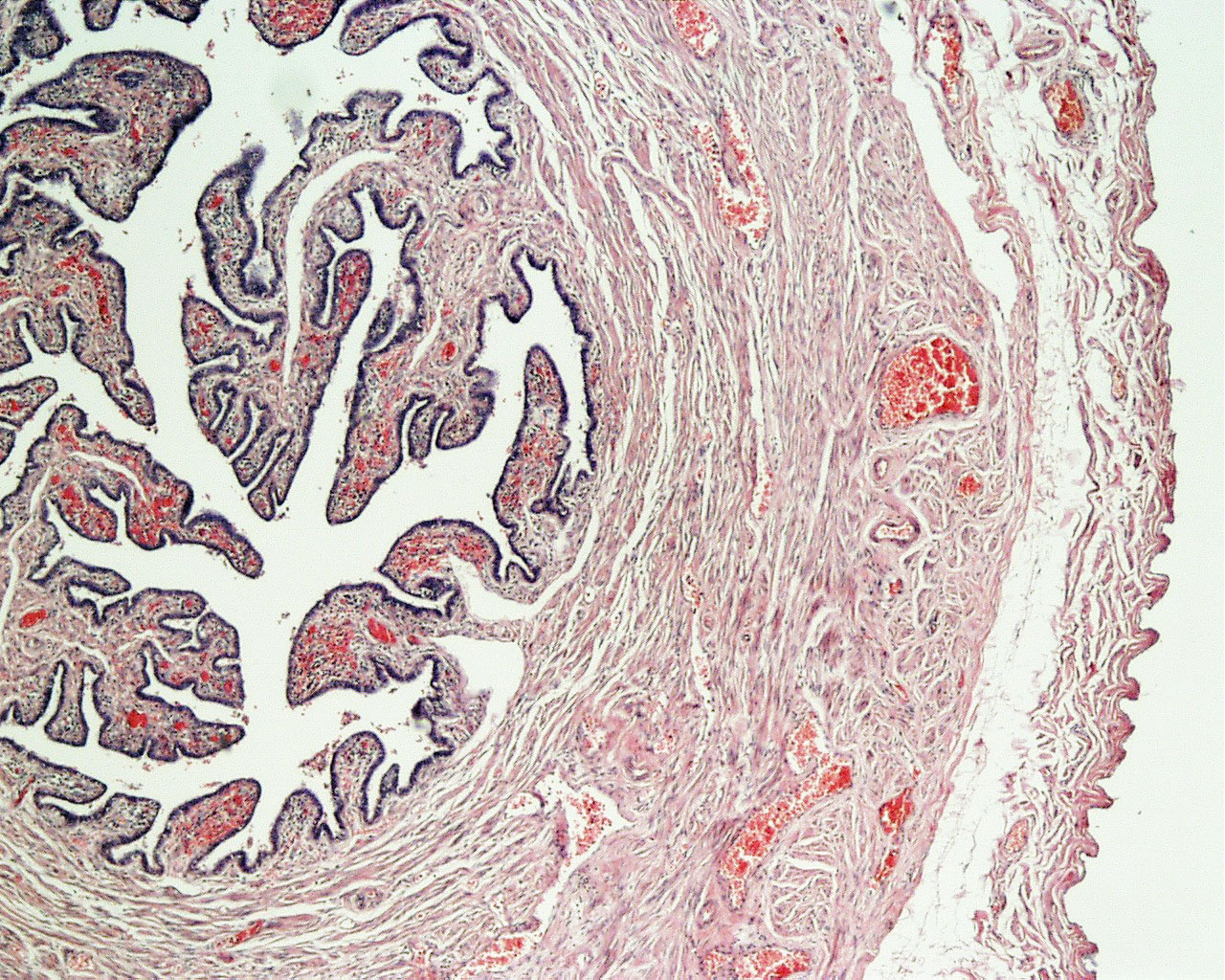
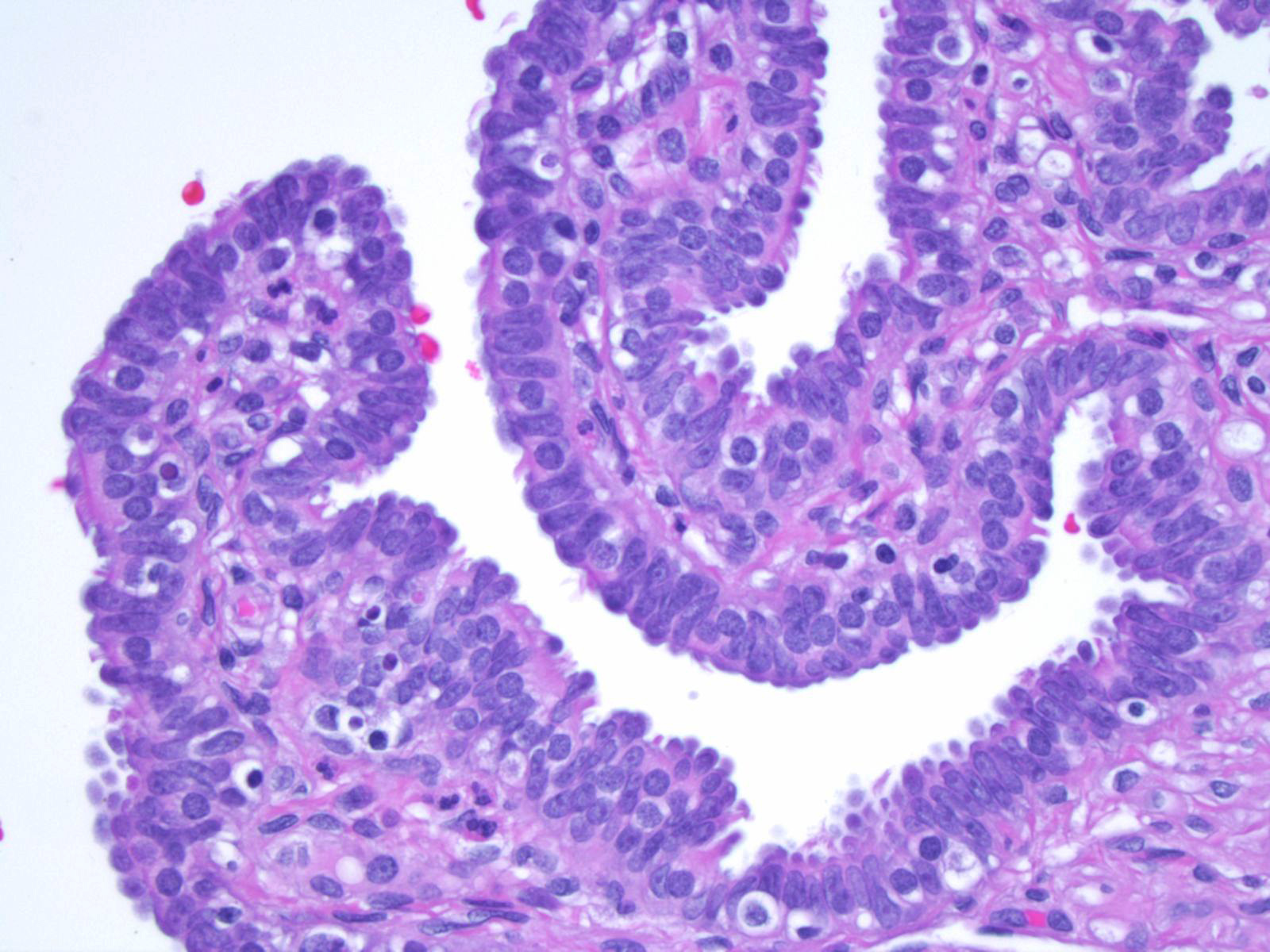
Histology at SIU Fallopian Tube A fallopian tube (also called uterine tube or oviduct) conducts each egg, following ovulation, from the ovary to the uterus. The wall of the fallopian tube includes an elaborately folded mucosa (endosalpinx) surrounded by a muscularis (myosalpinx).

HistoQuarterly FALLOPIAN TUBE Histology Blog
UTERUS UTERINE (FALLOPIAN) TUBES VAGINA PLACENTA MAMMARY GLANDS FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The female reproductive system consists of 2 ovaries, 2 oviducts (also known as uterine or fallopian tubes), the uterus, vagina, external genitalia and 2 mammary glands.

Dictionary Normal Fallopian tube Fallopian tubes, Glandular cells, Dictionary
Link of Instagram: https://instagram.com/knowing_anatomy?igshid=12mmn11n2pxe6The normal fallopian tube extends from the area of its corresponding ovary to it.

Online histology slides atlas Complete student friendly histology atlas Medic For You
Fallopian tubes & broad ligament General Anatomy, histology, embryology & features to report Authors: Nicole D. Riddle, M.D., Jamie Shutter, M.D. Last author update: 1 March 2013 Last staff update: 7 June 2022 Copyright: 2002-2024, PathologyOutlines.com, Inc. PubMed Search: Fallopian tubes - normal anatomy and histology Page views in 2023: 13,988
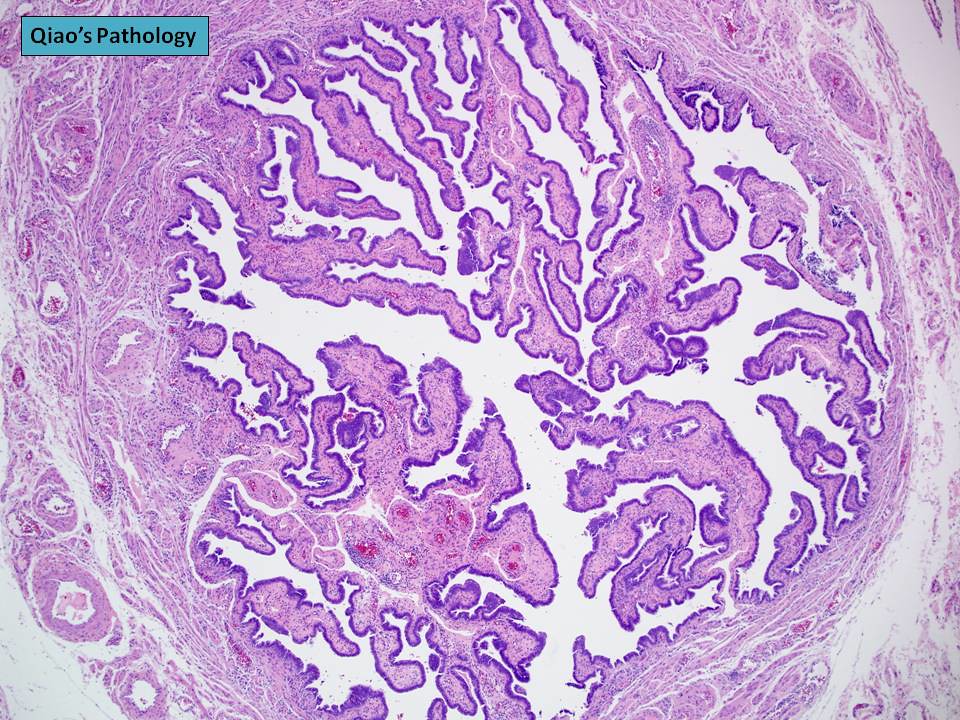
Qiao's Pathology Normal Fallopian Tube (乔氏病理学:正常输卵管) Flickr
1) the trapping of the egg, 2) a region where fertilization takes place, and 3) a region simply for transport to the uterus. Examine its open end near the ovary, the infundibulum View Image, in slide 240-1 and note the funnel shape and ridges of mucosa that extend as a fringe of finger-like projections known as fimbriae.
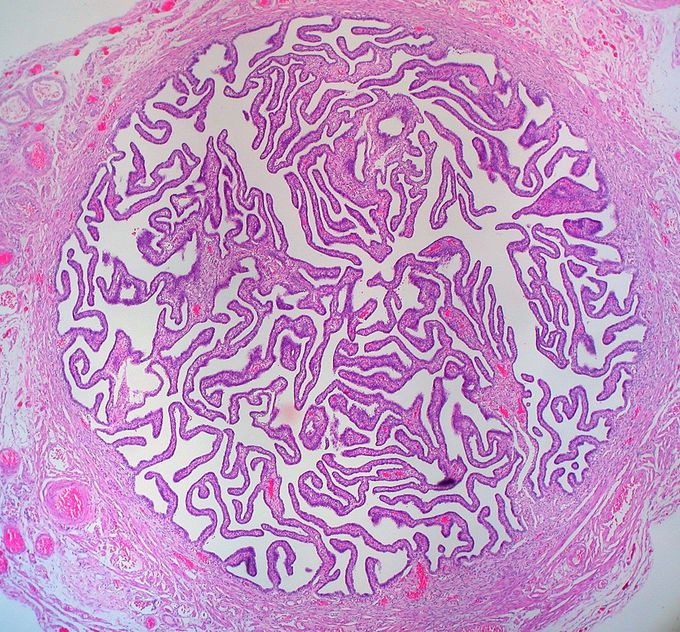
Histology of FALLOPIAN TUBE MEDizzy
A fallopian tube consists of a thin mucous membrane and layers of muscle. Mucous membrane: A delicate lining in your fallopian tubes secrete fluids that maintain an environment where fertilization can happen and an embryo can develop. Small hair-like structures in the lining (cilia) sway, moving eggs, sperm and an embryo (if fertilization takes.
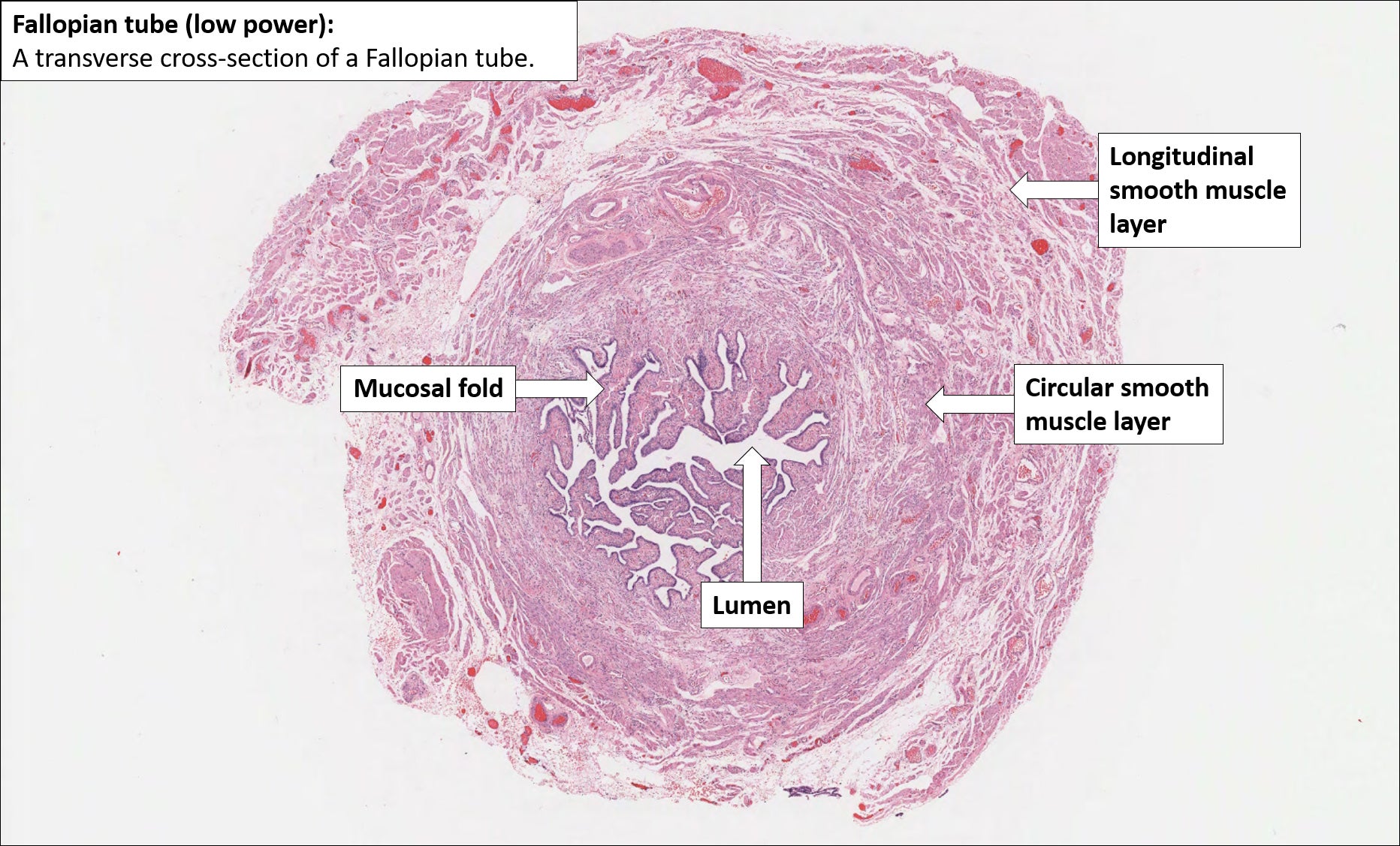
Fallopian tube Normal Histology NUS Pathweb NUS Pathweb
Fallopian histology slide labeled diagram Let's try to identify all the histological features from the actual slide sample with the help of the fallopian histology slide labeled diagram. Suggested slides for you - The ovary histology slide with a labeled diagram A proliferative and secretory uterus histology slide with the labeled diagrams

Active Learning for the Medical Sciences Draw It to Know It
Fallopian tube epithelial tumors: carcinosarcoma endometrioid adenocarcinoma high grade serous carcinoma serous adenofibroma and papilloma serous borderline tumor (pending) serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma Fallopian tube mixed epithelial and mesenchymal tumors: adenosarcoma (pending) Fallopian tube germ cell tumors: teratoma (pending)
Human Biology Online Lab / Copy of Fallopian Tubes by Elynn Johnson
Physiologic functions discussed in this article include the role of the fallopian tube in sperm transport, its part in sperm maintenance and capacitation, and the tube's function in ovum transport, fertilization, and embryo transport. Clinically, the role of the myosalpinx is undetermined, although it may affect tubal motility and ovum transport.
Pathology Outlines Anatomy, histology, embryology & features to report
The fallopian tubes are two thin tubes that extend from the uterus to the ovaries. They consist of 4 parts.
Fallopian tube Normal Histology NUS Pathweb NUS Pathweb
The fallopian tube ( TA: tuba uterina 8 ), also known as the uterine tube or, less commonly, the oviduct, is a paired hollow tube that bridges the ovary and uterus and functions to convey the mature ovum from the former to the latter. If conception occurs, it usually does so within the tube, which can be affected by a wide range of pathology.
Fallopian Tube Histology Labeled
fallopian tube, either of a pair of long narrow ducts located in the human female abdominal cavity that transport male sperm cells to the egg, provide a suitable environment for fertilization, and transport the egg from the ovary, where it is produced, to the central channel (lumen) of the uterus.. Each fallopian tube is 10-13 cm (4-5 inches) long and 0.5-1.2 cm (0.2-0.6 inch) in diameter.

Histology of Fallopian Tubes \ Uterine Tube YouTube
The uterine tubes (a.k.a. fallopian tubes) are important structures in the female reproductive tract, which connect the peritoneal cavity with the uterine cavity. They provide a site for fertilisation and are involved in the transport of the ovum from the ovaries to the body of the uterus. The uterine tubes are also referred to as the oviducts.
Pathology Outlines Anatomy, histology, embryology & features to report
The fallopian tubes are bilateral conduits between the ovaries and the uterus in the female pelvis. They function as channels for oocyte transport and fertilization. Given this role, the fallopian tubes are a common etiology of infertility as well as the target of purposeful surgical sterilization. They can also be sites of ascending infection or neoplasms.